


Next: The Fixed-Node Approximation
Up: Diffusion Quantum Monte Carlo
Previous: The Method
The algorithm used in the DMC calculations reported in this thesis
for solving Eq.( ) is illustrated in figure
) is illustrated in figure  .
It can be divided into the following steps:
.
It can be divided into the following steps:
Figure: Flow chart illustrating the DMC algorithm.
- Initialise a set of
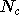 configurations (typically 100-500),
with configurations distributed according to a probability density
configurations (typically 100-500),
with configurations distributed according to a probability density
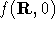 , given by
, given by 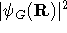 . These are generated
by choosing configurations produced in a VMC run. The configurations
are taken sufficiently far apart in the VMC run so as to ensure their
independence, using the procedure described in
section
. These are generated
by choosing configurations produced in a VMC run. The configurations
are taken sufficiently far apart in the VMC run so as to ensure their
independence, using the procedure described in
section  .
. - Each configuration in the list is taken in turn. The
electrons in the
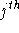 configuration are then moved, one at a time,
by letting them diffuse independently for a time
configuration are then moved, one at a time,
by letting them diffuse independently for a time  . If the
current electron is the
. If the
current electron is the 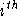 electron in configuration j, it is
moved according to
electron in configuration j, it is
moved according to
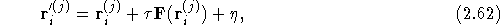
where 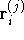 is the three-dimensional coordinate of the
electron being moved, and
is the three-dimensional coordinate of the
electron being moved, and 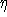 is a three-dimensional Gaussian
random variable with a mean of zero and a variance of
is a three-dimensional Gaussian
random variable with a mean of zero and a variance of  . The
time step
. The
time step  is chosen to be small enough so that the time
step error[30], introduced by the approximation to the
Green's function in Eq.(
is chosen to be small enough so that the time
step error[30], introduced by the approximation to the
Green's function in Eq.( ), is less than the
statistical uncertainty. Usually
), is less than the
statistical uncertainty. Usually  is chosen so that the rate of
acceptance of moves is
is chosen so that the rate of
acceptance of moves is 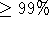 .
.
- The fixed-node approximation is now applied. We check to see
whether the move has caused the walker to cross the nodal surface. If
this has occurred we reject the move and go to the next electron on the
list.
- Now calculate a weight for the move,
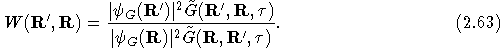
The move is then accepted with probability
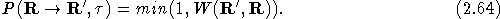
- After all the electrons in the
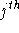 configuration have been moved
the time associated with this configuration is advanced by one time
step,
configuration have been moved
the time associated with this configuration is advanced by one time
step,  .
. - Calculate the branching probability for configuration j, using:
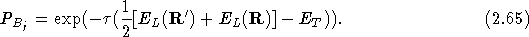
Then make

copies of the walker, where 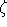 is a uniform random number in the range
[0,1].
is a uniform random number in the range
[0,1].
- If
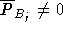 then weight
then weight 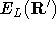 and
any other accumulated quantities by the branching probability,
and
any other accumulated quantities by the branching probability, 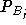 . This
branching probability is a measure of the importance weight of the walker.
. This
branching probability is a measure of the importance weight of the walker. -
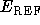 is an adjustable energy used to stabilise the
population of walkers.
is an adjustable energy used to stabilise the
population of walkers. 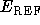 is recalculated according to
is recalculated according to
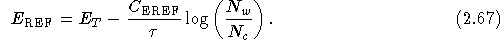
Where 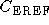 is a parameter adjusted so as to control
population fluctuations.
is a parameter adjusted so as to control
population fluctuations. 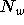 is the number of configurations at the
present time and
is the number of configurations at the
present time and 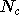 is the target number of configurations.
is the target number of configurations.
- Repeat steps (2) through to (8) for all the configurations for a
certain number of steps. Note that the total number of steps is
divided up into blocks. The number of steps in each block is chosen
such that the averages accumulated over the blocks of steps are
statistically independent. This block length usually corresponds to
diffusing each walker for a time of order a few atomic units.
- Calculate the weighted mean of
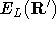 and all other
desired averages. It is not necessary to use the more complicated
scheme for updating the averages (section
and all other
desired averages. It is not necessary to use the more complicated
scheme for updating the averages (section  ) used in
VMC as the probability of accepting a given move is much higher
(99%) due to the smaller time step used in DMC calculations.
) used in
VMC as the probability of accepting a given move is much higher
(99%) due to the smaller time step used in DMC calculations. - Use the cumulative estimate of
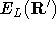 to update the
trial energy
to update the
trial energy 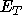 . We do this according to
. We do this according to 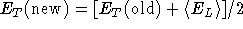 , where
, where 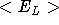 is the
block average of the energy. Note, the initial value of
is the
block average of the energy. Note, the initial value of 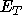 is
usually taken as the VMC energy for the same system.
is
usually taken as the VMC energy for the same system. - Renormalise the number of walkers to
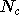 ; do this by randomly
removing walkers (
; do this by randomly
removing walkers ( 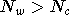 ), or creating copies of existing walkers (
), or creating copies of existing walkers ( 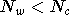 ), where
), where 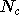 is the desired number of walkers.
is the desired number of walkers. - Repeat steps (2) to (12) until there is no longer a detectable
trend in the block average of
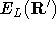 , i.e. the components of
excited eigenstates in the wavefunction have effectively decayed away
as shown in Eq.(
, i.e. the components of
excited eigenstates in the wavefunction have effectively decayed away
as shown in Eq.(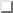 ). At this point the steady-state has
been reached.
). At this point the steady-state has
been reached. - Repeat steps (2) through to
(12) until the variance of the cumulative averages has reached the
desired level.
At the end of a DMC calculation the average values of 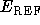 ,
,
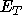 , and
, and 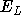 should be the same to within error bars.
should be the same to within error bars.
The output from an example DMC calculation is shown in
figure  . It illustrates the initial exponential decay
in the energy, taking place over the first 150 or so time steps, as
the contribution to the distribution, f, from the excited states
decays with time. When the graph levels out, the energy is
oscillating due to statistical noise. Averages for observable
quantities would be taken over the final 800 steps.
. It illustrates the initial exponential decay
in the energy, taking place over the first 150 or so time steps, as
the contribution to the distribution, f, from the excited states
decays with time. When the graph levels out, the energy is
oscillating due to statistical noise. Averages for observable
quantities would be taken over the final 800 steps.

It is useful to note that if the weights in step (4) are set to
as in VMC, the drift term is removed, and the branching
probabilities in step (7) are set to unity for all configurations, the
algorithm reduces back to the VMC algorithm already described. This
not only highlights the many similarities between the two algorithms,
but also provides a useful method of checking whether a DMC algorithm is
working correctly as it is can then be directly compared with known
VMC results.



Next: The Fixed-Node Approximation
Up: Diffusion Quantum Monte Carlo
Previous: The Method
Andrew Williamson
Tue Nov 19 17:11:34 GMT 1996
![]() ) is illustrated in figure
) is illustrated in figure ![]() .
It can be divided into the following steps:
.
It can be divided into the following steps:
![]()
![]() is the three-dimensional coordinate of the
electron being moved, and
is the three-dimensional coordinate of the
electron being moved, and ![]() is a three-dimensional Gaussian
random variable with a mean of zero and a variance of
is a three-dimensional Gaussian
random variable with a mean of zero and a variance of ![]() . The
time step
. The
time step ![]() is chosen to be small enough so that the time
step error[30], introduced by the approximation to the
Green's function in Eq.(
is chosen to be small enough so that the time
step error[30], introduced by the approximation to the
Green's function in Eq.(![]() ), is less than the
statistical uncertainty. Usually
), is less than the
statistical uncertainty. Usually ![]() is chosen so that the rate of
acceptance of moves is
is chosen so that the rate of
acceptance of moves is ![]() .
.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is a uniform random number in the range
[0,1].
is a uniform random number in the range
[0,1].![]() is a parameter adjusted so as to control
population fluctuations.
is a parameter adjusted so as to control
population fluctuations. ![]() is the number of configurations at the
present time and
is the number of configurations at the
present time and ![]() is the target number of configurations.
is the target number of configurations.![]() ,
,
![]() , and
, and ![]() should be the same to within error bars.
should be the same to within error bars.
![]() . It illustrates the initial exponential decay
in the energy, taking place over the first 150 or so time steps, as
the contribution to the distribution, f, from the excited states
decays with time. When the graph levels out, the energy is
oscillating due to statistical noise. Averages for observable
quantities would be taken over the final 800 steps.
. It illustrates the initial exponential decay
in the energy, taking place over the first 150 or so time steps, as
the contribution to the distribution, f, from the excited states
decays with time. When the graph levels out, the energy is
oscillating due to statistical noise. Averages for observable
quantities would be taken over the final 800 steps.
![]()