Requesting polarization
Polarization is a fundamental property that is not easy to define and calculate in an infinite solid. CASTEP implements the Berry phase approach to define spontaneous polarization unambiguously. For a comprehensive explanation of the modern theory of polarization, see Spaldin (2012) .
If the task is Elastic Constants, CASTEP applies predefined strains to the original structure, optimizes atomic coordinates in the deformed structures, and calculates spontaneous polarization. CASTEP then uses calculated values of polarization to evaluate the piezoelectric strain tensor, through numerical differentiation of polarization with respect to applied strain:

The piezoelectric strain tensor is related to the piezoelectric stress tensor, through the elastic coefficients tensor that connects strain and stress responses:
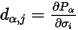
In the full unfolded form of these tensors, the connection is:
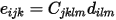
Polarization calculations are not allowed if you use any of the following settings:
- Ultra-soft pseudopotentials
- Spin-polarized calculation
- DFT+U
- Spin-orbit coupling with non-collinear spins
- External electric field
- Mixture atoms
To request calculation of polarization
- Choose Modules | CASTEP | Calculation from the menu bar to display the CASTEP Calculation dialog.
- Select the Properties tab.
- Check the Polarization checkbox in the list of properties.